Metabolische Netzwerke deuten auf intelligentes Design
https://elshaddai.forumotion.com/t131-metabolischen-netzwerke-deuten-auf-intelligentes-design
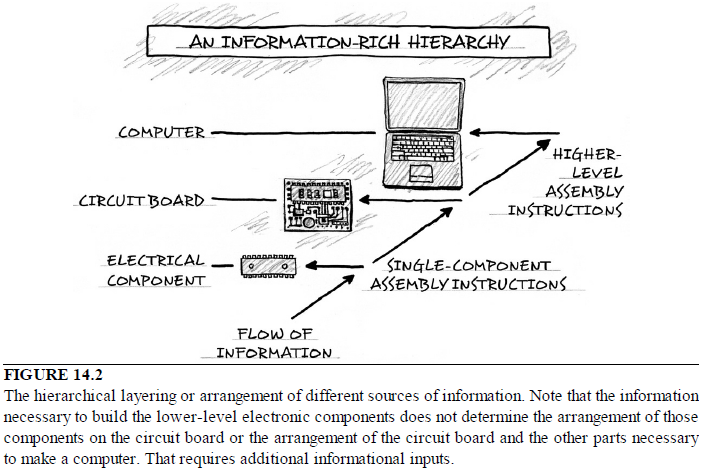
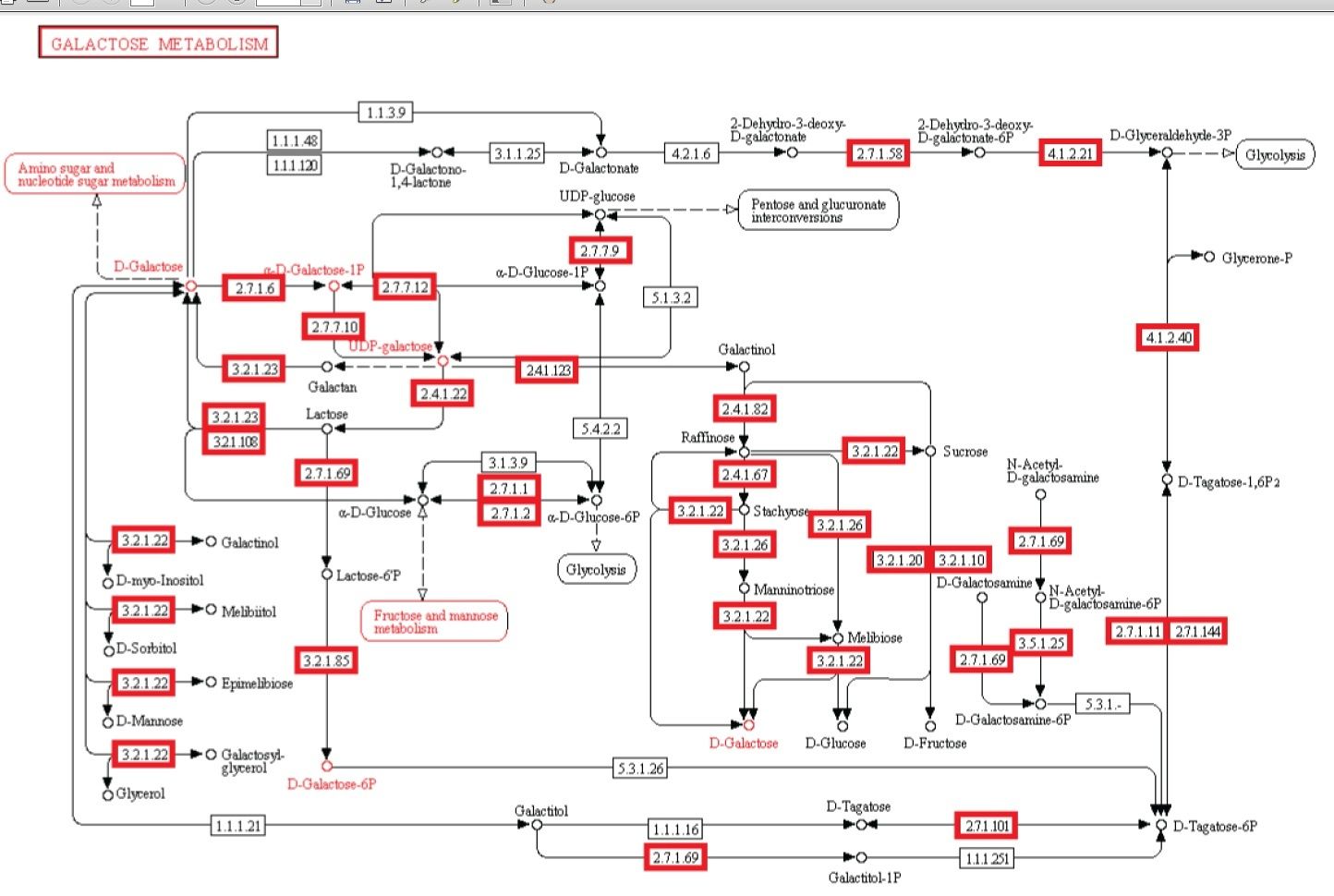
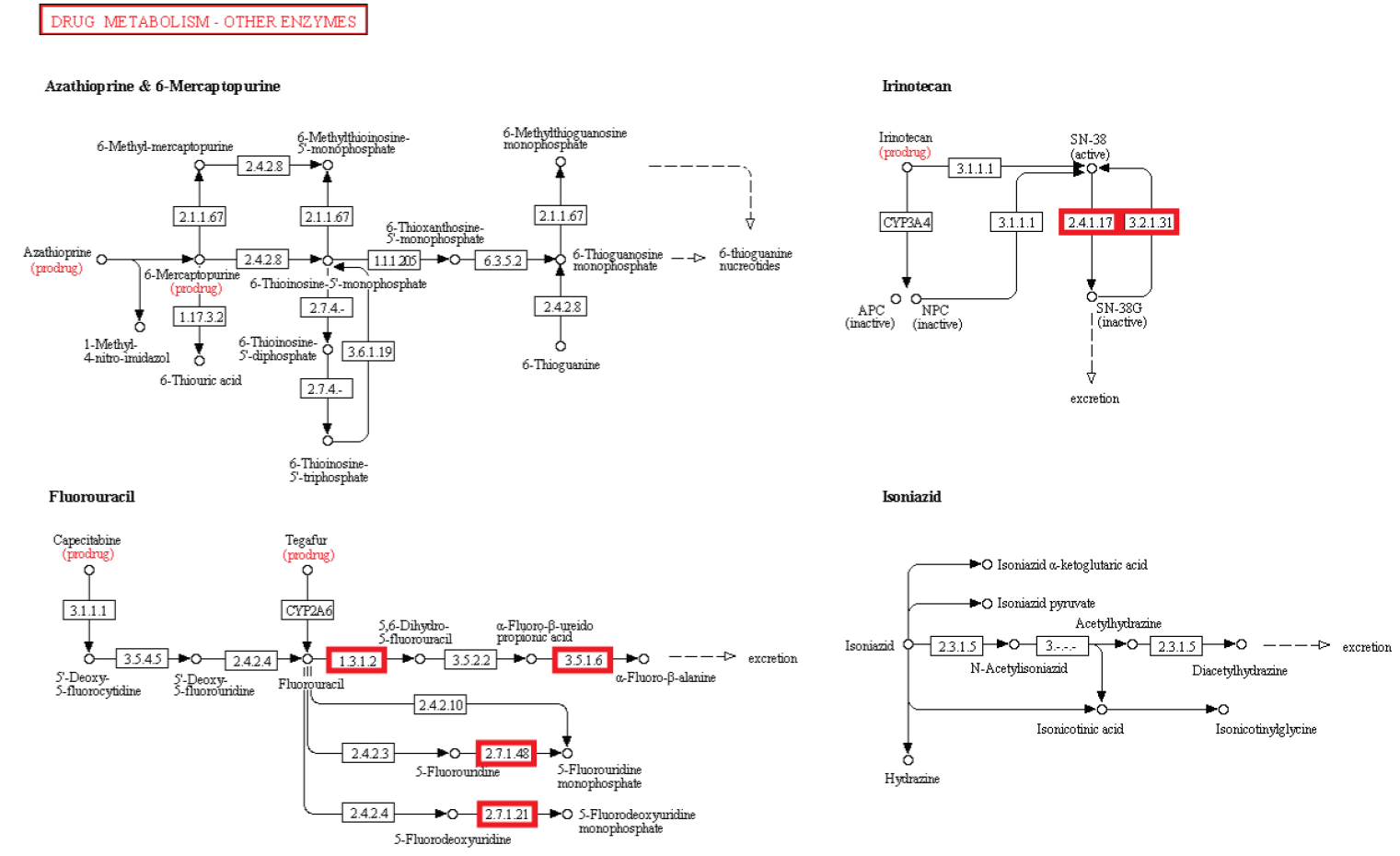
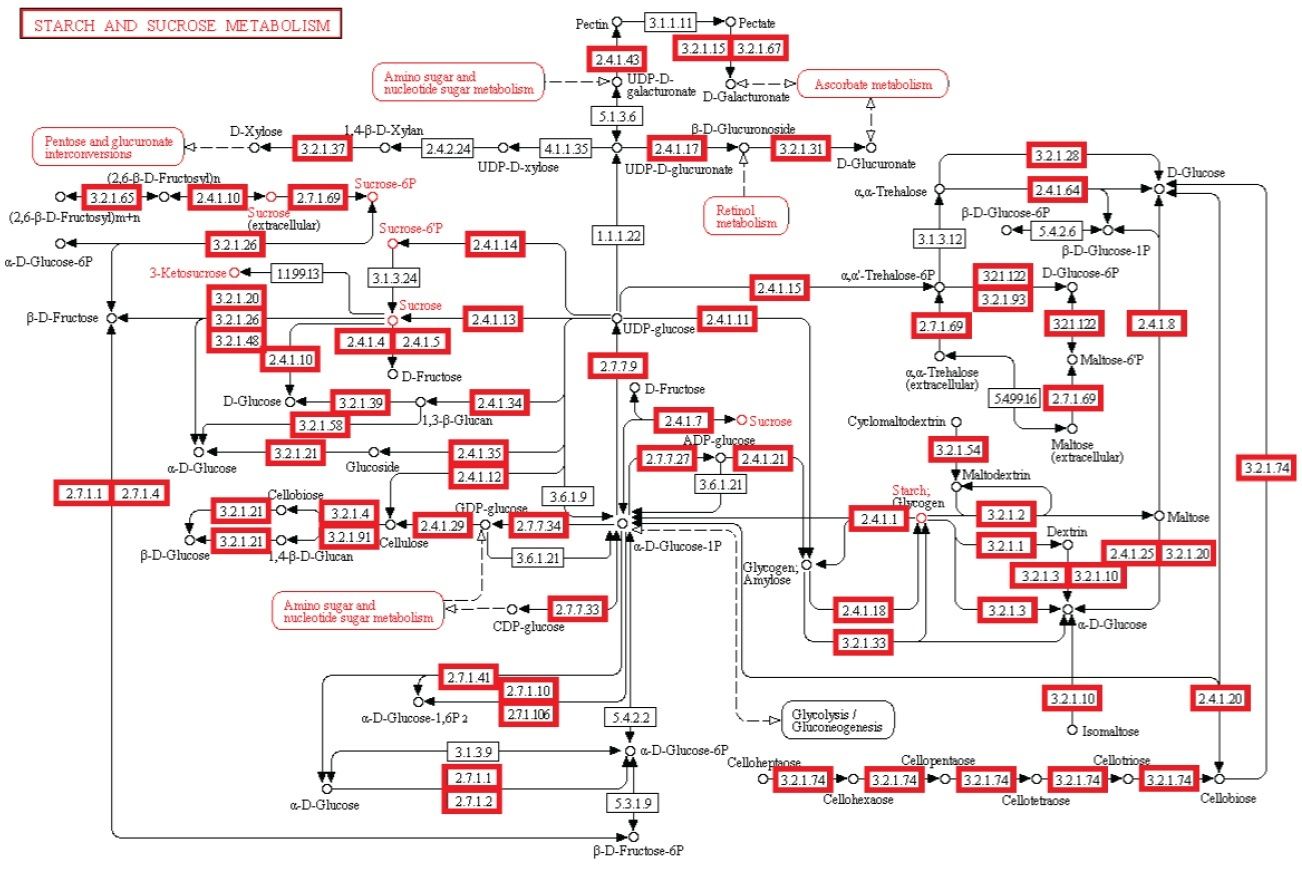
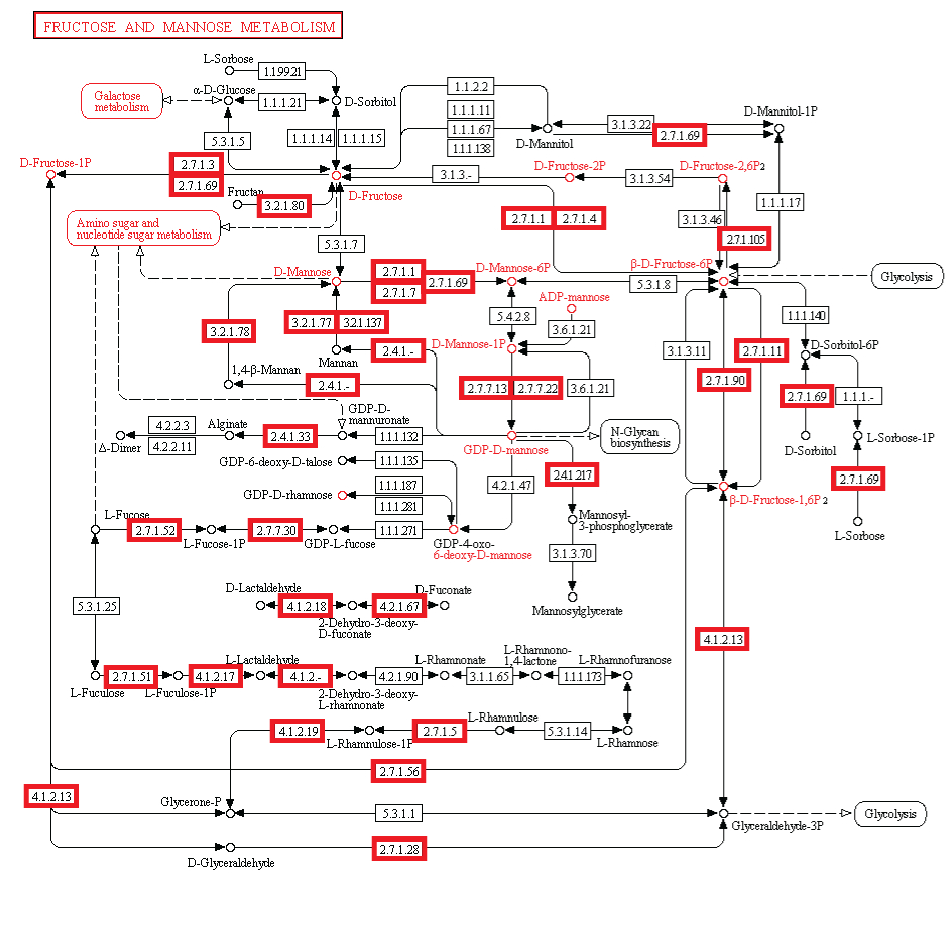
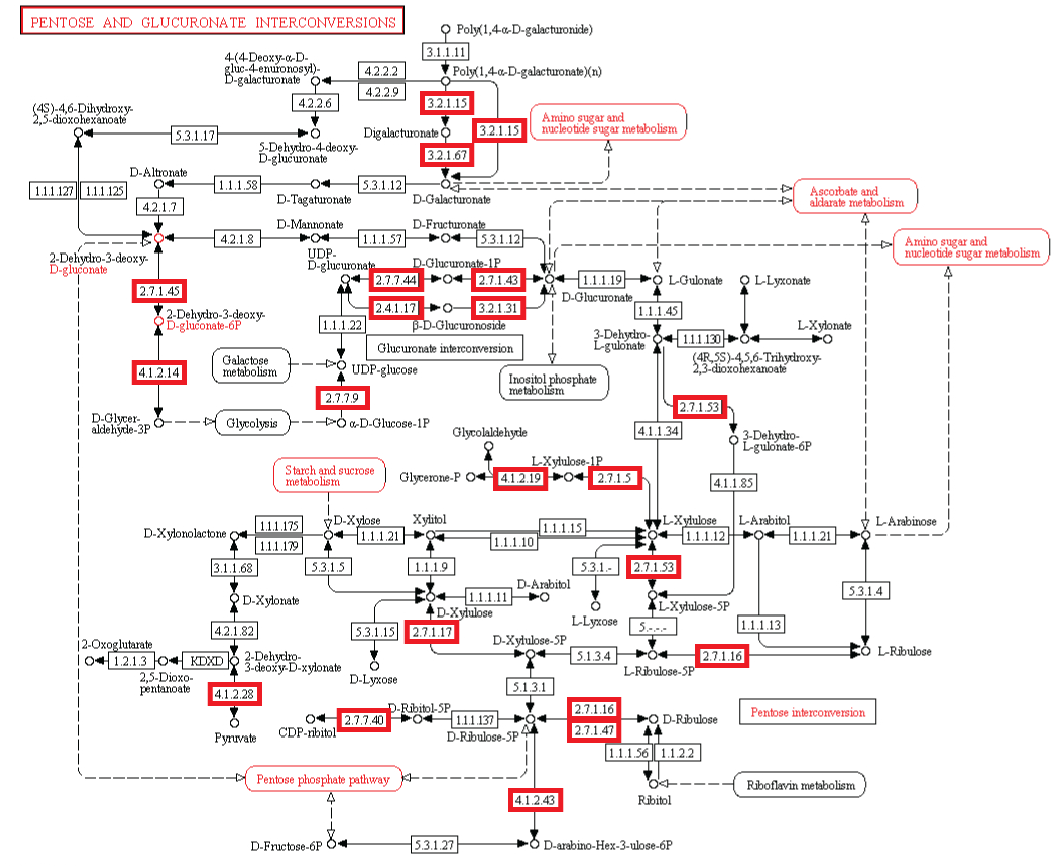
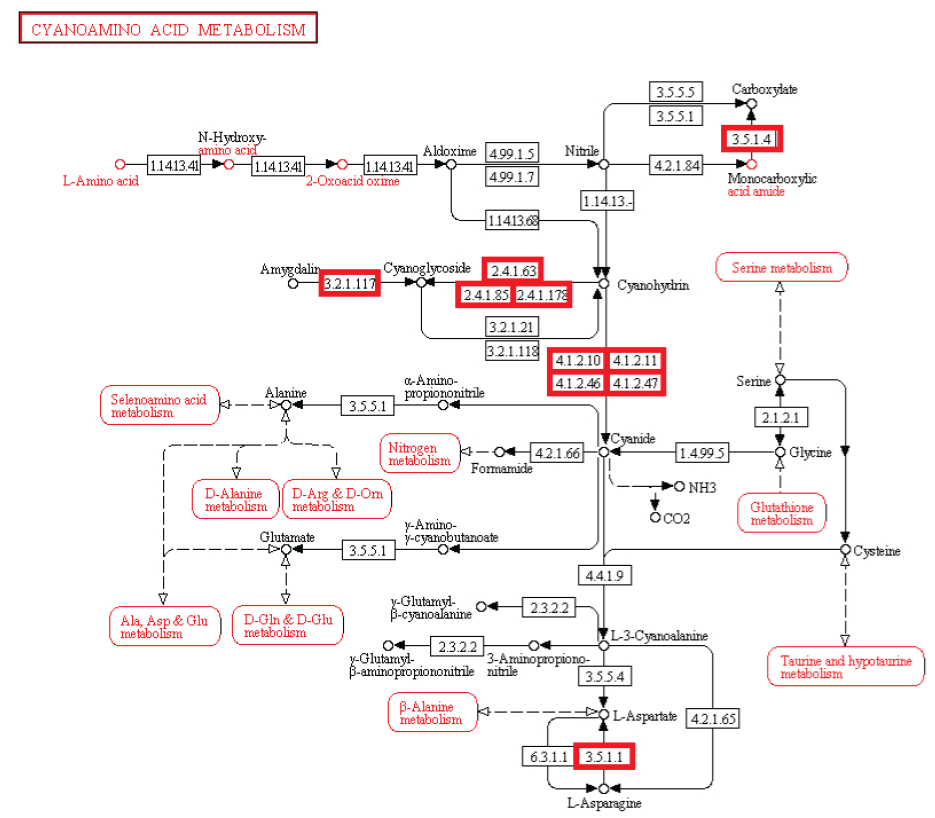
Beobachtung: Die Existenz von Stoffwechselwegen ist von entscheidender Bedeutung für molekulare und zelluläre Funktionen, und lebensnotwendig für die Zelle. Metabolische Netzwerke kann man sich wie eine Leiterplatte eines Computers oder eine Schaltzentrale vorstellen. Obwohl bakterielle Genome sich in beträchtlichem Ausmaß in ihrer Größe und Gen-Repertoires unterscheiden, egal wie klein, müssen sie alle Informationen enthalten, um der Zelle zu ermöglichen, viele essentielle (Housekeeping) Funktionen auszuführen, die der Zelle die Fähigkeit der metabolischen Homöostase geben, zu reproduzieren, und sich an die Umwelt anzupassen. Das sind die drei wichtigsten Eigenschaften lebender Zellen . (Gil et al. 2004) In der Tat ist Metabolismus eines der konserviertesten Zellprozesse. Mit Daten aus vergleichender Genomik und groß Deletionsstudien, hat der wissenschaftliche Artikel "Strukturelle Analysen eines hypothetischen minimalen Stoffwechsels "
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2442391/#bib12
ein minimales Gen-Set bestehend aus 206 Protein-kodierenden Genen für eine hypothetische minimale Zelle vorgeschlagen. Das Papier enthält und nennt 50 Enzyme/Proteine, welche benötigt werden, um ein metabolisches Netzwerk von einem hypothetischen Minimalgenom für die hypothetische minimale Zelle zu erstellen. Die 50-Enzyme/Proteine und das metabolische Netzwerk müssen vollständig sein, um einer Zelle zu ermöglichen, die Grundfunktionen zu halten.
Hypothese (Vorhersage): Der Ursprung der biologischen der nicht reduzierbaren Stoffwechselwege, die auch Regulierung erfordern und die wie eine Kaskade aufgebaut sind, ähnlich wie bei elektronischen Leiterplatten, werden am besten durch die kreative Wirkung eines intelligenten Agenten erklärt
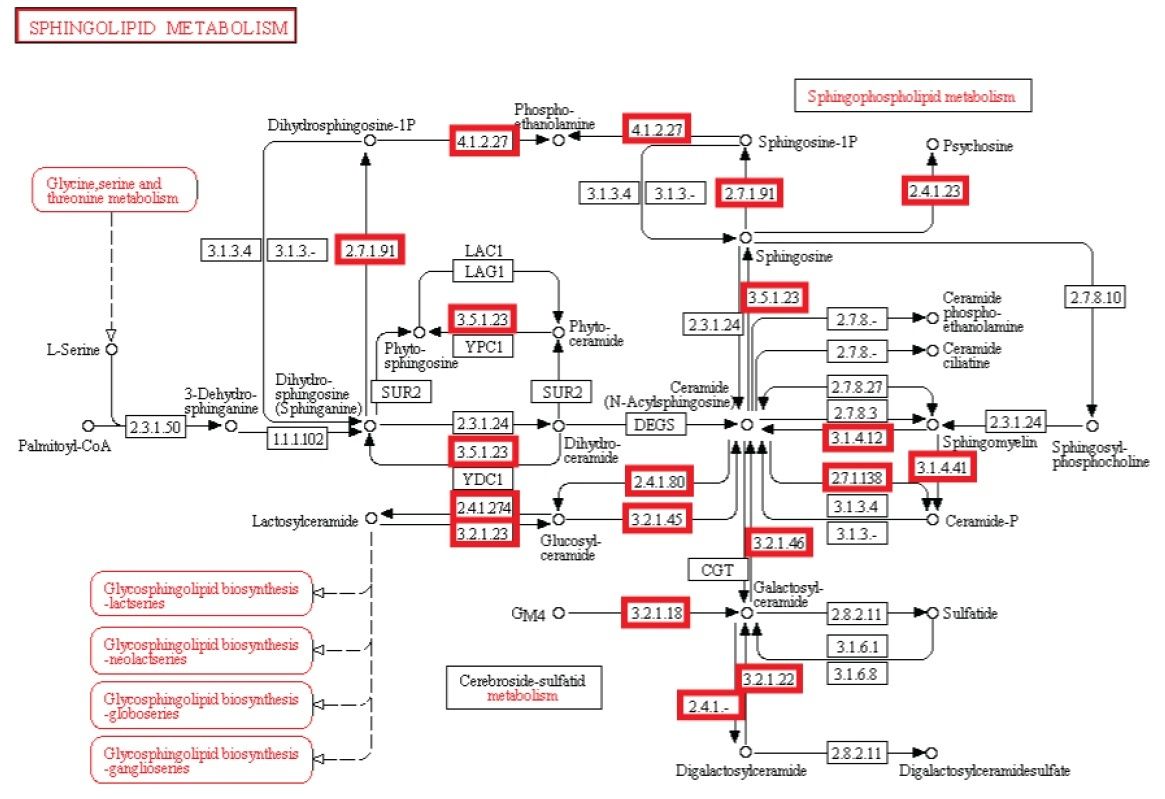
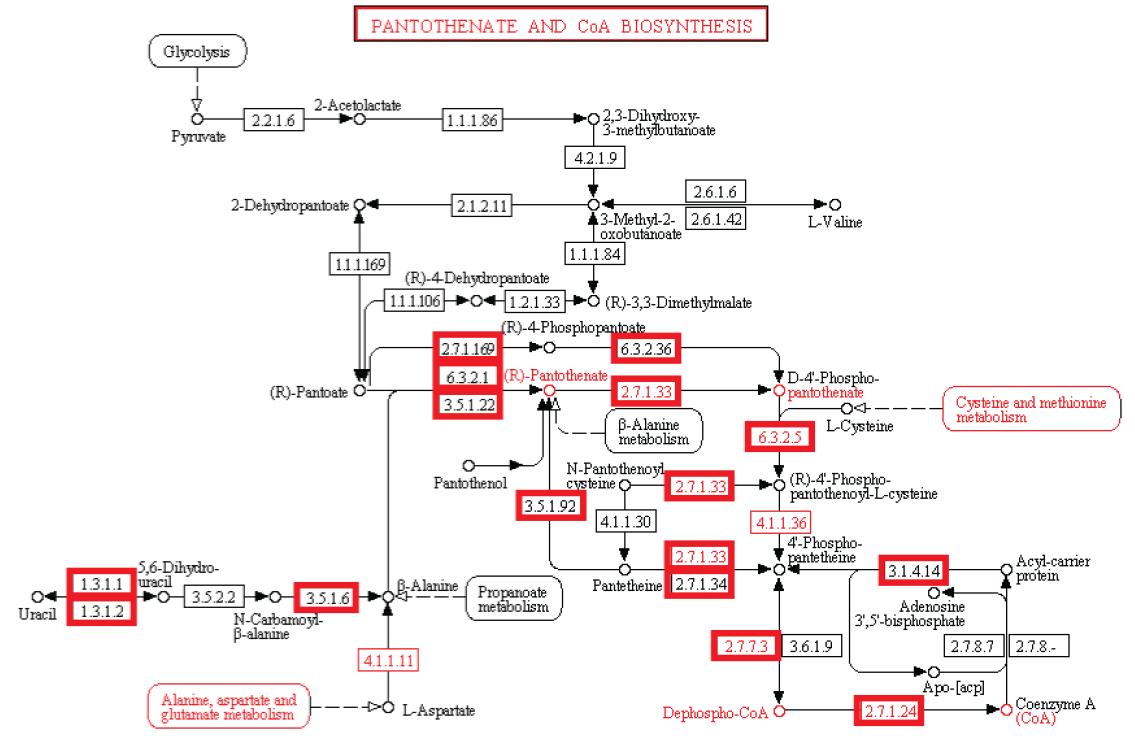
Experiment: Experimentelle Untersuchungen von metabolischen Netzwerken zeigen, dass diese voll von Knotenpunkten/Verzweigungen mit Enzymen/Proteinen sind, (die für ihre Synthese Informationen benötigen gespeichert im DNA) Hierarchische Strukturen sind notwendig, um die meisten Funktionen von metabolischen Netzwerken auszuführen (Ravasz et al, 2002). Es hat sich gezeigt, dass Stoffwechselprodukte nur hergestellt werden können, wenn Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff, Phosphor und Schwefel und die Grundbausteine, durch diese Elemente erzeugt durch den zentralen Stoffwechsel, zur Verfügung stehen. Dies bedeutet, dass regulatorische Netzwerke metabolischer Aktivitäten auf die Verfügbarkeit dieser grundlegenden Ressourcen beruhen und von ihnen abhängig sind. So eine Stoffwechsel-Schaltung hängt von den Produkten ab, die von zentralen Stoffwechselwegen kommen, das eine vom anderen abhängig, wie in einer Kaskade. Außerdem ist es nennenswert, dass um den metabolischen Fluss zu regulieren, Rückkopplungsschleifen benötigt werden. Diese sind in einer funktionellen Weise miteinander verbunden, und für eine lebende Zelle notwendig. Die biologischen Stoffwechsel-Netzwerke sind exquisit integriert, so dass Veränderungen zwangsläufig zu beschädigter oder zerstörter Funkion führen Änderungen im Fluss erfordern oft Änderungen in den Aktivitäten mehrerer Enzyme in einer metabolischen Sequenz. Synthese eines Metaboliten erfordert typischerweise die Inbetriebnahme von vielen Wegen.
Schlussfolgerung: Unabhängig von seiner anfänglichen Komplexität, kann selbsterhaltendes leben auf Basis chemischer metabolischer Netzwerke nicht erzeugt werden ohne der Existenz eines Erbmechanismus, welcher für die Wartung, die Stabilität und die Diversifizierung ihrer Komponenten notwendig ist. Bei der Ermangelung würden Auto-trophische Reaktionsketten kommen und gehen, ohne dass es möglich sein würde, irgendwelche direkten Nachkommen zu generieren, um den Prozess wieder zu beleben. Leben, wie wir wissen, besteht sowohl aus Chemie und Informationen. Wenn es metabolische präbiotische Prozesse gab, um diese in komplexes Leben zu verwandeln wie wir es kennen, bräuchte es auch die Erschaffung eines genetischen replizierenden Mechanismus, (Ribas de Poupkna, Ph.D.)
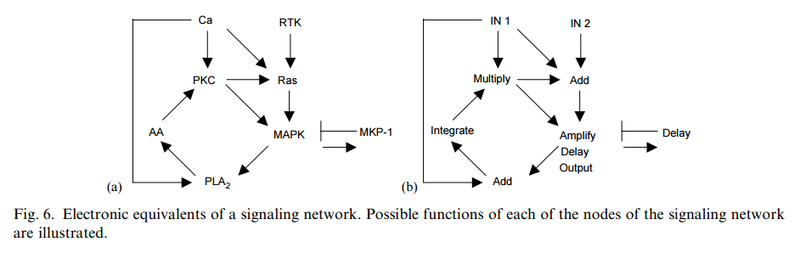
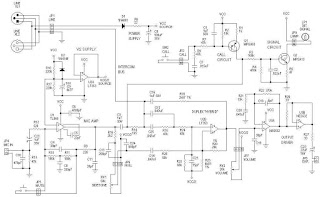
Intelligente Agenten haben häufig Ziele vor Augen, und verwenden ein hohes Maß komplexer Informationen, um ein bestimmtes Ziel zu erreichen. Unserer Erfahrung nach stammen Systeme welche große Mengen an instruierender komplexer Informationen speichern durch Codes und Sprachen, wie Bücher, Morsecodes, Computercodes, Partituren, - immer von einer intelligenten Quelle. Ebenso Schaltungen oder Netzwerke von koordinierten Interaktion wie zum Beispiel von analogen elektronischen Geräten können immer zu einem intelligenten Erzeuger zurückgeführt werden. Der Betrieb der analogen elektronischen Vorrichtungen entspricht sehr eng dem Informationsfluss in chemischen Reaktionen von Stoffwechselwegen (McAdams und Shapiro, 1995). Eine vorgeschlagener Mechanismus muss in der Lage sein, de novo metabolische Netzwerke zu erschaffen, eine minimale Menge von 50 Enzymen und komplexen integrierten metabolischen Schaltungen, mit dem klaren Endziel vor Augen, Lebern zu erschaffen. Ein metabolisches Netzwerk, das nicht voll funktionsfähig ist, wird Leben nicht ermöglichen Wir wissen, in unserer Erfahrung, dass Intelligenz zur Erschaffung von Leiterplatten der Lage ist, wie diskrete elektronische Platinen, und ist die einzige bekannte Ursache komplexer Bauteile, wie Schaltungen, Kapazitoren, Kondensern etc, die man mit Enzymen vergleichen kann. Da die Evolution von voll funktionstüchtigen metabolischen Schaltungen abhängig ist, ist sie als möglicher Mechanismus ausgeschlossen. Da bleiben nur zwei Alternativen Zufall/Glück oder physische Notwendigkeit. Diese werden jedoch nie in der Lage sein, Leiterplatten und funktionelle aufeinander abgestimmte Enzyme herzustellen. Das wurde noch nie beobachtet. Und die Chance, dass dies durch Zufall passieren könnte, ist so groß, dass es im Bereich des unmöglichen liegt. Der Ursprung der metabolischen Netzwerke der ersten Zellen wird daher durch die Wirkung eines intelligenten Agenten am besten erklärt.
Instruierende komplexe kodierte Information in epigenetischen Systemen und Genen gespeichert, und nicht reduzierbar, voneinander abhängige molekulare Maschinen und Biosynthetische und Stoffwechselwege in biologischen Systemen weisen auf die Anforderung eines intelligenten Agenten, um ihre Erschaffung und Herkunft zu erklären.
Beobachtung: Intelligente Agenten können mit einem Endziel vor Augen, funktional komplexe mehrteilige Maschinen konstruieren, die einen Bauplan und ein Projekt erfordern , sowie ein hohes Maß an komplexer instruktiver kodierter Information (kiki). Unserer Erfahrung gemäß kann man den Ursprung von Systemen, die entweder große Mengen an kiki wie Codes und Sprachen a) verwenden oder b) speichern - immer auf einen intelligenten Ursprung zurückverfolgen .
Hypothese (Vorhersage): Natürliche Strukturen werden gefunden werden, welche in komplizierten Mustern und nicht reduzierbaren Strukturen angeordnet sind welche viele Teile enthalten, die eine bestimmte Funktion erfüllen - welche ein hohes maß von (kiki) und irreduzibler Komplexität beinhalten.
Experiment: Experimentelle Untersuchungen von DNA, epigenetischer Codes, biosynthetischer Wege und metabolischer Schaltungen zeigen, dass sie reiche kiki, sprach basierte Codes beinhalten und auf Code/Plan basierende Strukturen. Biologen haben Mutationsempfindlichkeitstests an Proteinen durchgeführt und festgestellt, dass die Aminosäuresequenzen, um Proteinfunktion zu erhalten, ein hohes mass an kiki benoetigen, welches im gen gespeichert ist. Zusätzlich wurde herausgefunden, dass die Zelle verschiedene epigenetische Codes enthält, nämlich die Splicing-Codes, die Metabolic-Codes, Signal Transduktion Codes, Signalintegrations Codes, den Histon-Code, den Tubulin-Code, den Zucker-Code und den glycomic-Code. Darüber hinaus sind alle Art von irreduzibel komplexe molekulare Maschinen, Biosynthese und Stoffwechselwege gefunden wurden, die nicht ihre Grundfunktionen und Prozesse ohne eine minimale Anzahl von Teilen und Komponenten halten können Das beweist, diese biologischen Maschinen und Prozesswege mussten voll funktionsfähig entstehen, auf einmal. Eine schrittweise evolutionsartige Entwicklung ist nicht möglich. Darüber hinaus haben knock out Experimente aller Komponenten der Geißel gezeigt, dass diese per Definition nicht reduzierbar komplex ist.
Fazit: Es sei denn, jemand kann die Vorhersage falsifizieren, und auf eine nicht-intelligente Quelle für komplexe kodierte Informationen hinweisen, die hohe kiki in biochemischen Systemen erzeugen kann, und molekulare Systeme und biologische Prozesswege, die nicht reduzierbar und voneinander abhängig sind , ist ihre Herkunft am besten durch die Wirkung eines intelligenten Agenten erklärt.
Originaltext : http://reasonandscience.heavenforum.org/t2371-how-cellular-enzymatic-and-metabolic-networks-point-to-design
https://elshaddai.forumotion.com/t131-metabolischen-netzwerke-deuten-auf-intelligentes-design

Beobachtung: Die Existenz von Stoffwechselwegen ist von entscheidender Bedeutung für molekulare und zelluläre Funktionen, und lebensnotwendig für die Zelle. Metabolische Netzwerke kann man sich wie eine Leiterplatte eines Computers oder eine Schaltzentrale vorstellen. Obwohl bakterielle Genome sich in beträchtlichem Ausmaß in ihrer Größe und Gen-Repertoires unterscheiden, egal wie klein, müssen sie alle Informationen enthalten, um der Zelle zu ermöglichen, viele essentielle (Housekeeping) Funktionen auszuführen, die der Zelle die Fähigkeit der metabolischen Homöostase geben, zu reproduzieren, und sich an die Umwelt anzupassen. Das sind die drei wichtigsten Eigenschaften lebender Zellen . (Gil et al. 2004) In der Tat ist Metabolismus eines der konserviertesten Zellprozesse. Mit Daten aus vergleichender Genomik und groß Deletionsstudien, hat der wissenschaftliche Artikel "Strukturelle Analysen eines hypothetischen minimalen Stoffwechsels "
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2442391/#bib12
ein minimales Gen-Set bestehend aus 206 Protein-kodierenden Genen für eine hypothetische minimale Zelle vorgeschlagen. Das Papier enthält und nennt 50 Enzyme/Proteine, welche benötigt werden, um ein metabolisches Netzwerk von einem hypothetischen Minimalgenom für die hypothetische minimale Zelle zu erstellen. Die 50-Enzyme/Proteine und das metabolische Netzwerk müssen vollständig sein, um einer Zelle zu ermöglichen, die Grundfunktionen zu halten.
Hypothese (Vorhersage): Der Ursprung der biologischen der nicht reduzierbaren Stoffwechselwege, die auch Regulierung erfordern und die wie eine Kaskade aufgebaut sind, ähnlich wie bei elektronischen Leiterplatten, werden am besten durch die kreative Wirkung eines intelligenten Agenten erklärt
Experiment: Experimentelle Untersuchungen von metabolischen Netzwerken zeigen, dass diese voll von Knotenpunkten/Verzweigungen mit Enzymen/Proteinen sind, (die für ihre Synthese Informationen benötigen gespeichert im DNA) Hierarchische Strukturen sind notwendig, um die meisten Funktionen von metabolischen Netzwerken auszuführen (Ravasz et al, 2002). Es hat sich gezeigt, dass Stoffwechselprodukte nur hergestellt werden können, wenn Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff, Phosphor und Schwefel und die Grundbausteine, durch diese Elemente erzeugt durch den zentralen Stoffwechsel, zur Verfügung stehen. Dies bedeutet, dass regulatorische Netzwerke metabolischer Aktivitäten auf die Verfügbarkeit dieser grundlegenden Ressourcen beruhen und von ihnen abhängig sind. So eine Stoffwechsel-Schaltung hängt von den Produkten ab, die von zentralen Stoffwechselwegen kommen, das eine vom anderen abhängig, wie in einer Kaskade. Außerdem ist es nennenswert, dass um den metabolischen Fluss zu regulieren, Rückkopplungsschleifen benötigt werden. Diese sind in einer funktionellen Weise miteinander verbunden, und für eine lebende Zelle notwendig. Die biologischen Stoffwechsel-Netzwerke sind exquisit integriert, so dass Veränderungen zwangsläufig zu beschädigter oder zerstörter Funkion führen Änderungen im Fluss erfordern oft Änderungen in den Aktivitäten mehrerer Enzyme in einer metabolischen Sequenz. Synthese eines Metaboliten erfordert typischerweise die Inbetriebnahme von vielen Wegen.
Schlussfolgerung: Unabhängig von seiner anfänglichen Komplexität, kann selbsterhaltendes leben auf Basis chemischer metabolischer Netzwerke nicht erzeugt werden ohne der Existenz eines Erbmechanismus, welcher für die Wartung, die Stabilität und die Diversifizierung ihrer Komponenten notwendig ist. Bei der Ermangelung würden Auto-trophische Reaktionsketten kommen und gehen, ohne dass es möglich sein würde, irgendwelche direkten Nachkommen zu generieren, um den Prozess wieder zu beleben. Leben, wie wir wissen, besteht sowohl aus Chemie und Informationen. Wenn es metabolische präbiotische Prozesse gab, um diese in komplexes Leben zu verwandeln wie wir es kennen, bräuchte es auch die Erschaffung eines genetischen replizierenden Mechanismus, (Ribas de Poupkna, Ph.D.)
Intelligente Agenten haben häufig Ziele vor Augen, und verwenden ein hohes Maß komplexer Informationen, um ein bestimmtes Ziel zu erreichen. Unserer Erfahrung nach stammen Systeme welche große Mengen an instruierender komplexer Informationen speichern durch Codes und Sprachen, wie Bücher, Morsecodes, Computercodes, Partituren, - immer von einer intelligenten Quelle. Ebenso Schaltungen oder Netzwerke von koordinierten Interaktion wie zum Beispiel von analogen elektronischen Geräten können immer zu einem intelligenten Erzeuger zurückgeführt werden. Der Betrieb der analogen elektronischen Vorrichtungen entspricht sehr eng dem Informationsfluss in chemischen Reaktionen von Stoffwechselwegen (McAdams und Shapiro, 1995). Eine vorgeschlagener Mechanismus muss in der Lage sein, de novo metabolische Netzwerke zu erschaffen, eine minimale Menge von 50 Enzymen und komplexen integrierten metabolischen Schaltungen, mit dem klaren Endziel vor Augen, Lebern zu erschaffen. Ein metabolisches Netzwerk, das nicht voll funktionsfähig ist, wird Leben nicht ermöglichen Wir wissen, in unserer Erfahrung, dass Intelligenz zur Erschaffung von Leiterplatten der Lage ist, wie diskrete elektronische Platinen, und ist die einzige bekannte Ursache komplexer Bauteile, wie Schaltungen, Kapazitoren, Kondensern etc, die man mit Enzymen vergleichen kann. Da die Evolution von voll funktionstüchtigen metabolischen Schaltungen abhängig ist, ist sie als möglicher Mechanismus ausgeschlossen. Da bleiben nur zwei Alternativen Zufall/Glück oder physische Notwendigkeit. Diese werden jedoch nie in der Lage sein, Leiterplatten und funktionelle aufeinander abgestimmte Enzyme herzustellen. Das wurde noch nie beobachtet. Und die Chance, dass dies durch Zufall passieren könnte, ist so groß, dass es im Bereich des unmöglichen liegt. Der Ursprung der metabolischen Netzwerke der ersten Zellen wird daher durch die Wirkung eines intelligenten Agenten am besten erklärt.
Instruierende komplexe kodierte Information in epigenetischen Systemen und Genen gespeichert, und nicht reduzierbar, voneinander abhängige molekulare Maschinen und Biosynthetische und Stoffwechselwege in biologischen Systemen weisen auf die Anforderung eines intelligenten Agenten, um ihre Erschaffung und Herkunft zu erklären.
Beobachtung: Intelligente Agenten können mit einem Endziel vor Augen, funktional komplexe mehrteilige Maschinen konstruieren, die einen Bauplan und ein Projekt erfordern , sowie ein hohes Maß an komplexer instruktiver kodierter Information (kiki). Unserer Erfahrung gemäß kann man den Ursprung von Systemen, die entweder große Mengen an kiki wie Codes und Sprachen a) verwenden oder b) speichern - immer auf einen intelligenten Ursprung zurückverfolgen .
Hypothese (Vorhersage): Natürliche Strukturen werden gefunden werden, welche in komplizierten Mustern und nicht reduzierbaren Strukturen angeordnet sind welche viele Teile enthalten, die eine bestimmte Funktion erfüllen - welche ein hohes maß von (kiki) und irreduzibler Komplexität beinhalten.
Experiment: Experimentelle Untersuchungen von DNA, epigenetischer Codes, biosynthetischer Wege und metabolischer Schaltungen zeigen, dass sie reiche kiki, sprach basierte Codes beinhalten und auf Code/Plan basierende Strukturen. Biologen haben Mutationsempfindlichkeitstests an Proteinen durchgeführt und festgestellt, dass die Aminosäuresequenzen, um Proteinfunktion zu erhalten, ein hohes mass an kiki benoetigen, welches im gen gespeichert ist. Zusätzlich wurde herausgefunden, dass die Zelle verschiedene epigenetische Codes enthält, nämlich die Splicing-Codes, die Metabolic-Codes, Signal Transduktion Codes, Signalintegrations Codes, den Histon-Code, den Tubulin-Code, den Zucker-Code und den glycomic-Code. Darüber hinaus sind alle Art von irreduzibel komplexe molekulare Maschinen, Biosynthese und Stoffwechselwege gefunden wurden, die nicht ihre Grundfunktionen und Prozesse ohne eine minimale Anzahl von Teilen und Komponenten halten können Das beweist, diese biologischen Maschinen und Prozesswege mussten voll funktionsfähig entstehen, auf einmal. Eine schrittweise evolutionsartige Entwicklung ist nicht möglich. Darüber hinaus haben knock out Experimente aller Komponenten der Geißel gezeigt, dass diese per Definition nicht reduzierbar komplex ist.
Fazit: Es sei denn, jemand kann die Vorhersage falsifizieren, und auf eine nicht-intelligente Quelle für komplexe kodierte Informationen hinweisen, die hohe kiki in biochemischen Systemen erzeugen kann, und molekulare Systeme und biologische Prozesswege, die nicht reduzierbar und voneinander abhängig sind , ist ihre Herkunft am besten durch die Wirkung eines intelligenten Agenten erklärt.
Originaltext : http://reasonandscience.heavenforum.org/t2371-how-cellular-enzymatic-and-metabolic-networks-point-to-design
Last edited by ElShaddai888 on Wed Jul 27, 2016 4:58 am; edited 10 times in total